The Internet is continuously expanding! There is a significant amount of stress on network servers as a result of the billions of people that use the Internet. This is due to both the increased availability of devices for usage as well as the increased number of Web users. Many distinct technologies are totally dependent on the Internet. This applies to all of our VoIP calls, distant servers, web applications, and cloud storage. You don’t need to invest in robust and expensive resources to ensure that your end-user experience and service quality are greater. All you need to do is to focus on network optimization.
What is Network Optimization?
Network optimization is the process of maximizing the performance of a network while minimizing costs and maximizing the scalability & reliability of the network. It is achieved using advanced tools and algorithms to analyze and optimize the network infrastructure, configurations, and protocols. The goal is to identify and resolve bottlenecks, improve network utilization and ensure optimal data flow. It is also important to note that network optimization should also be a continuous process, as the network environment and its requirements are constantly changing. It should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in traffic patterns and changing business requirements. By implementing network optimization, the organization can ensure that its network is running at peak performance, providing a reliable and efficient service, which in turn will improve overall productivity and business performance.
Benefits of Optimization
The core benefits of network optimization are: And finally, Network optimization can lower expenses by maximizing efficiency and lowering resource utilization.
Network Optimization Metrics
A detailed assessment of the present state is required before any network can be optimized. Here are the crucial parameters to take into account while monitoring your network operations to get you started and focus on the most pertinent areas.
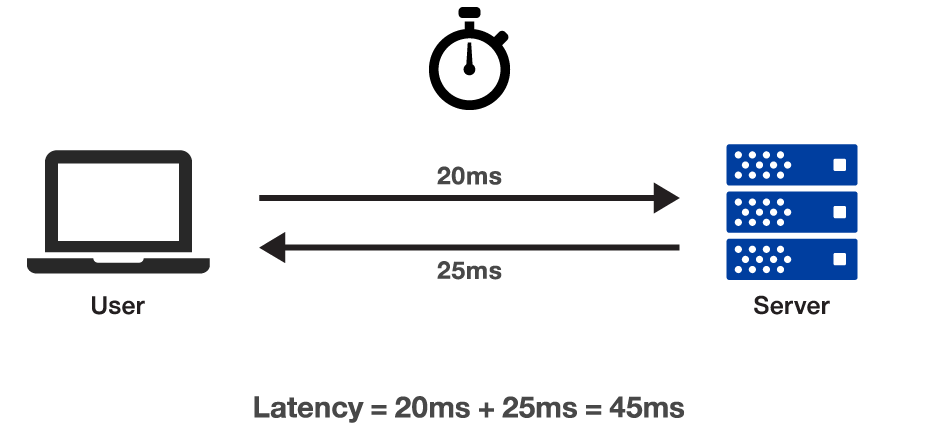
Latency
Latency is the amount of time it takes for a data packet to travel from its source to its destination. It is measured in milliseconds (ms). High latency can cause various issues, including dropped connections, corrupted video/audio streams, and delayed response times. These problems can be frustrating for users and can negatively impact the performance of applications. It’s crucial to pinpoint the cause of the issue and take action to minimize it in order to reduce latency. And here is a detailed guide on how to troubleshoot network latency.
Packet Loss
Data packets are small data units that are sent and received when accessing the internet or any other network. Packet loss occurs when one or more of these network packets are unable to reach their intended location, resulting in information loss. A small amount of packet loss is considered normal as it can happen due to network congestion or as a result of interference and other temporary conditions. However, if packet loss occurs regularly, it can severely impact network performance and must be addressed promptly.
Network Jitter
Jitter refers to the variation in the time it takes for data packets to travel from the sender to the receiver. Simply put, it is the deviation in the delay of the arrival of consecutive packets. It can be caused by several factors, including network congestion, queuing delays at network devices, and inconsistent network paths. Jitter can have a negative impact on real-time communication applications such as VoIP, video conferencing, and online gaming. These types of applications are sensitive to jitter because they require low latency and consistent delay in order to function properly.
Error rate
This metric measures the number of errors that occur on the network, such as corrupted packets or incorrect routing. High error rates indicate an issue with the network infrastructure or configurations.
Bandwidth Utilization
Measuring and monitoring the amount of bandwidth being used on the network can help to identify potential issues with network congestion and to ensure that there is enough capacity to meet the needs of users and applications. By understanding how these metrics are affected by different types of traffic flow, Network administrators can identify problem areas and bottlenecks in the network and take steps to improve performance.
What affects network performance?
A network’s performance can be affected by a variety of factors.
Network architecture
The way a network is designed and configured can have a big impact on its performance. Factors such as the number and placement of routers, switches, and other network devices can affect latency, throughput, and reliability.
Network Security
A network that is not properly secured can be vulnerable to attack, which can cause delays, data loss, and other problems.
Traffic
The amount of traffic on the network, including the number of users and the types of applications they are using, can also affect network performance.
Bandwidth
The amount of available bandwidth is a key factor in network performance. If there is not enough bandwidth to support the amount of traffic on the network, data transfer rates will be slow, and responses may be delayed.
Network Optimization Techniques
Let’s look at some network optimization methods you can implement to enhance network performance.
#1. Traffic shaping and bandwidth control
Bandwidth control involves allocating a specific amount of bandwidth to each user or device on the network. This can be done by setting a maximum data transfer rate for each user or device and monitoring the network to ensure these limits are not exceeded.
#2. Load balancing
By distributing network traffic across multiple servers or devices, companies can ensure that their network remains operational even if one or more devices become overloaded.
#3. Implementing Quality of Service (QoS)
It involves managing and prioritizing network traffic based on the type and level of service required by different applications. It is a way of ensuring that critical network traffic, such as voice/ video streaming, receives priority over less critical traffic, like file downloads and web browsing.
#4. Continuous monitoring
By monitoring the network performance and identifying patterns & trends, administrators can proactively identify and resolve potential issues before they become major disruptions. Here are a list best real-time bandwidth monitors for tracking network traffic usage.
#5. Data Compression
When data is compressed, it is transformed into a smaller representation that uses less space to store or transmit the same information. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be sent over the network, which can lead to faster response times.
#6. Router optimization
Configuring routers and switches to improve routing efficiency and reduce congestion on a network.
#7. Data Caching
Storing frequently requested data in a local cache reduces the load on the network and improves response times.
#8. Device Maintenance
Regular maintenance of devices and equipment on the network is necessary to ensure that they function properly and that any problems are quickly identified and resolved. These are just a few examples of the techniques that can be used to optimize a network. The key is to identify which methods are most appropriate for the network environment and to apply them strategically and systematically to achieve the desired results.
Learning Resources
And here are some additional resources you can use to learn about network optimization.
#1. Network Optimization: Continuous and Discrete Models
This book covers a wide range of topics related to network optimization, including optimization models and algorithms. It also provides clear information on discrete and combinatorial network optimization problems, including branch-and-bound and cutting-plane algorithms. The author has provided numerous examples and case studies to illustrate the concepts discussed, making it easy to understand how the methods and techniques can be applied in practice.
#2. Stochastic Network Optimization
This technical book provides a modern and in-depth analysis of network optimization and its applications to communication & queueing systems. It presents the mathematical techniques of Lyapunov drift and Lyapunov optimization that are developed to enable constrained optimization of time averages in general stochastic systems It provides a thorough introduction to the field and offers a lot of practical information that can be applied in real-world situations.
#3. Network Science: Analysis and Optimization Algorithms
This book comprehensively introduces network science and its applications, including network analysis, modeling, and optimization. It covers a wide range of topics, including graph theory, network topology, and centrality measures, as well as optimization algorithms such as gradient descent, linear assignment, minimum-cost network flow, and many more. The book is suitable for both students and professionals and provides a good balance between theory and practice. It is also a great resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of network optimization.
Conclusion
Bandwidth monitoring tools can be useful for monitoring and improving network performance. These tools can provide detailed visibility into the network’s performance, including metrics such as bandwidth usage, response times, and error rates. This information can be used to identify bottlenecks, optimize the use of resources, and troubleshoot issues. I hope you found this article helpful in learning about network optimization and the techniques to improve it. You may also be interested in learning about the best agentless network monitoring tools.

![]()